China aims to produce clean energy through "artificial sun"
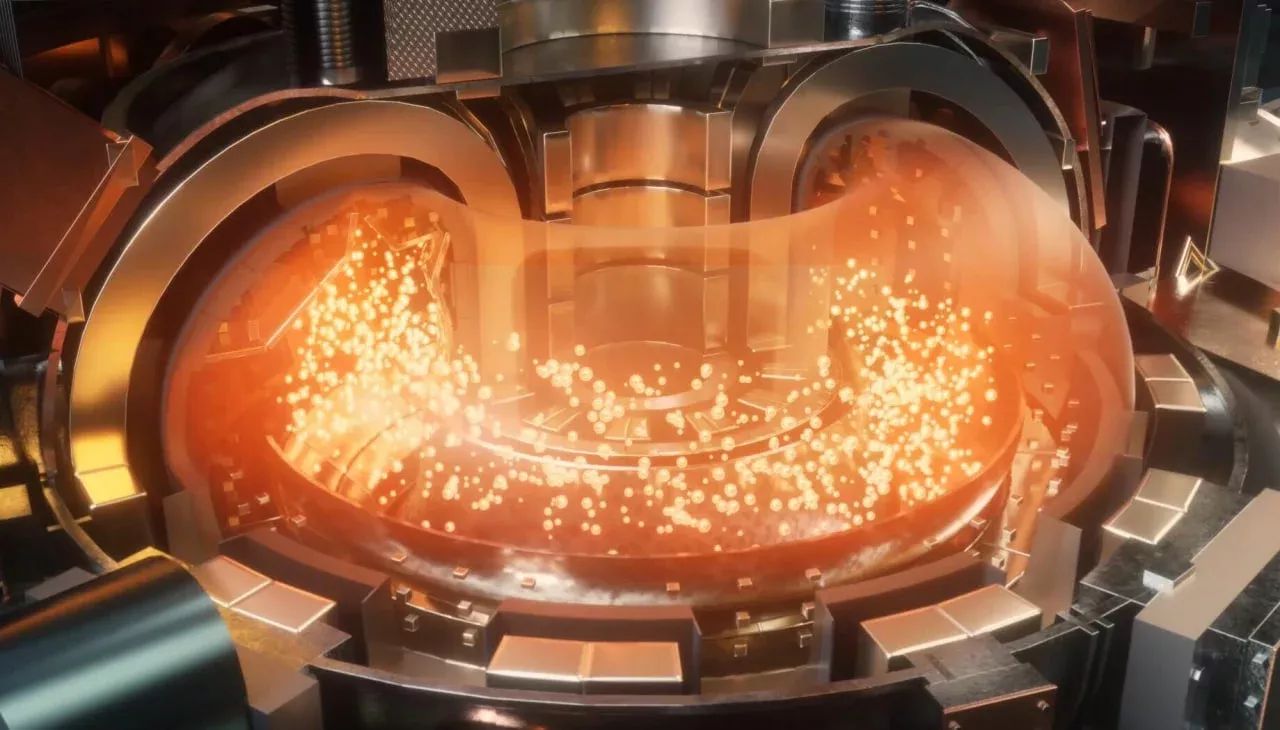
China plans to implement thermonuclear fusion technology with the goal of producing clean and limitless energy by 2050. According to Bloomberg, this technology will be realized through a tokamak device known as the "artificial sun".
Thermonuclear technology and China's goals
The tokamak device uses powerful magnetic fields to contain superheated plasma and sustain thermonuclear reactions. This technology aims to artificially replicate the thermonuclear reactions that occur in the natural Sun and stars. In 2023, China invested 240 million dollars into this project and plans to further strengthen scientific research in this area in the future.
Global thermonuclear research
So far, only countries like the USA, Russia, and South Korea have achieved significant breakthroughs in the field of thermonuclear fusion. However, China is mobilizing its vast scientific and technical capabilities to become one of the leading countries in this technology. Additionally, Beijing has also set goals to increase the production of small modular reactors and to expand the number of traditional nuclear power plants.
Advantages of thermonuclear fusion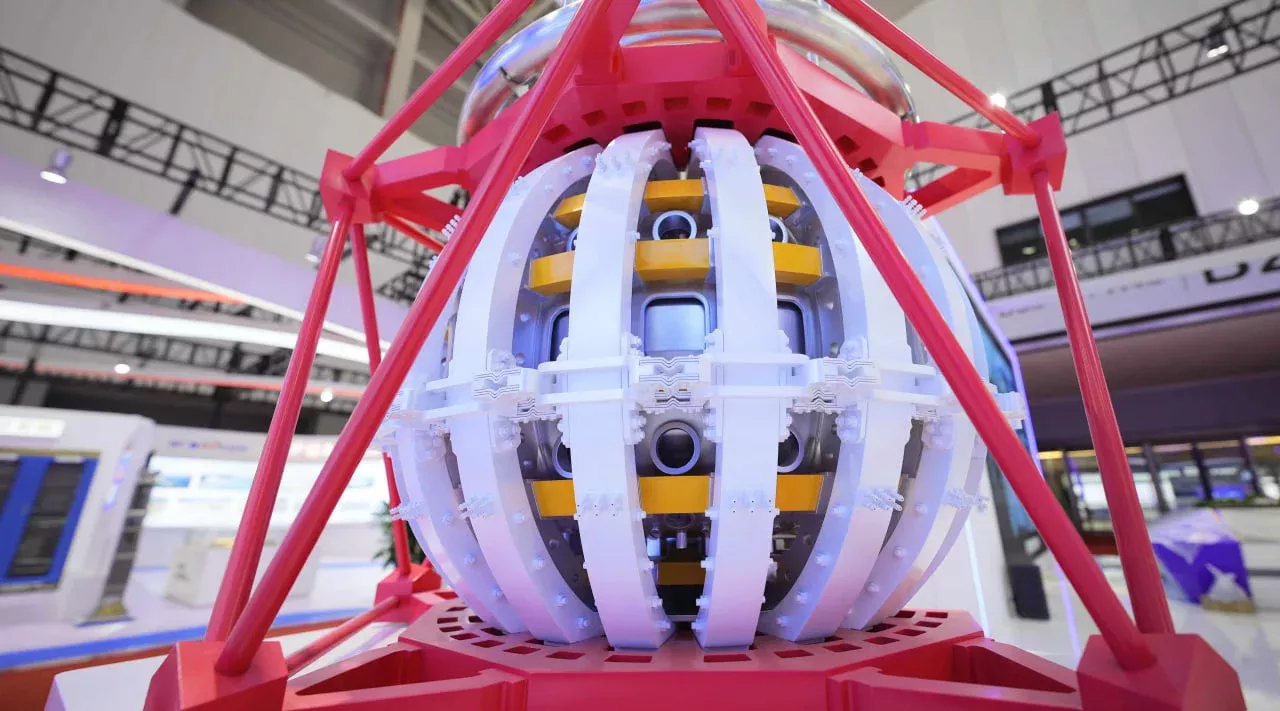
Thermonuclear fusion is a process in which energy is released as a result of the fusion of light atomic nuclei. This mechanism is based on the functioning of the Sun and stars. Compared to traditional nuclear energy, thermonuclear reactions have several advantages:
No radioactive waste produced – this could be a globally eco-friendly energy source.
Almost limitless energy source – as this process utilizes isotopes like deuterium and tritium, which are abundant in nature.
High efficiency – there is the potential to produce large amounts of energy as a result of thermonuclear reactions.
China's efforts to develop thermonuclear fusion technology are of immense significance not only for the country but for all humanity. If this technology is fully developed by 2050, it could provide a clean and limitless energy source on a global scale. This could be a crucial step in reducing carbon emissions, slowing down climate change, and addressing the energy crisis in the future.







