Tueyts glacier melting is increasing global risk
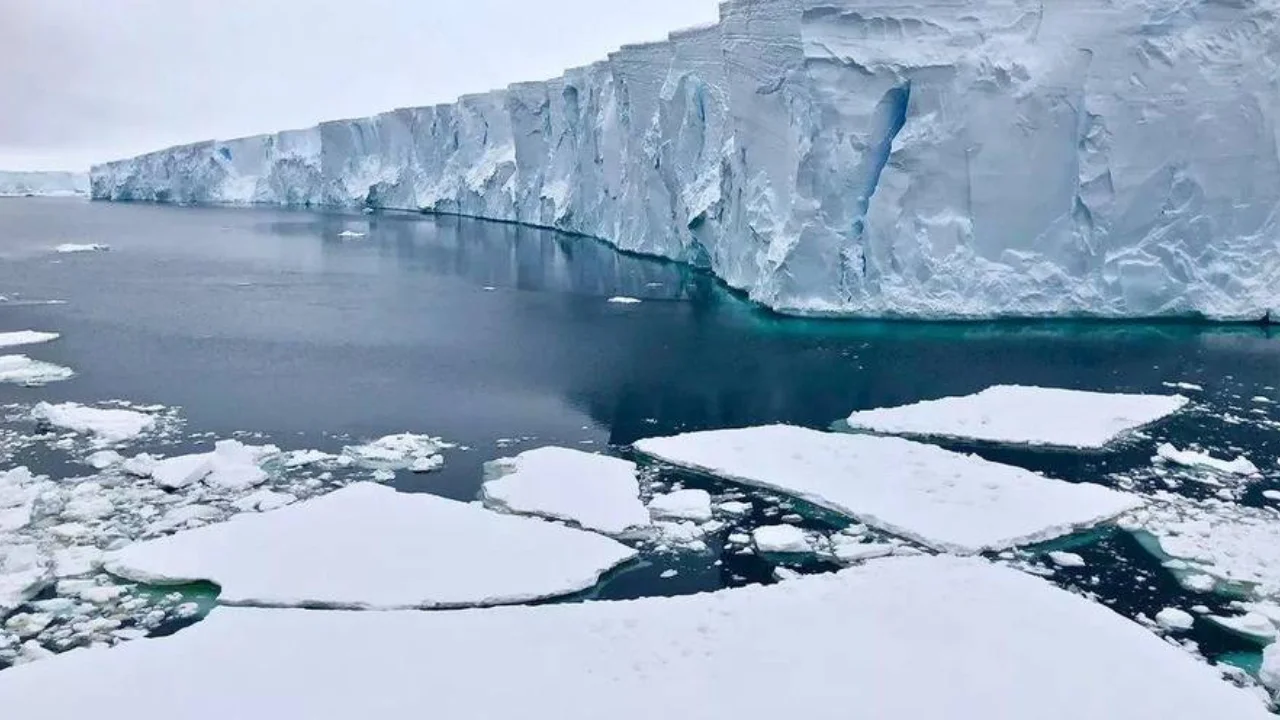

The Thwaites Glacier in Antarctica, also known as the "Doomsday Glacier," is rapidly melting, causing serious concern among scientists. This was reported by Zamin.uz.
According to research, if this massive ice sheet completely breaks apart and falls into the ocean, sea levels could rise by 1–2 meters. This situation increases the risk of major cities such as New York, London, Amsterdam, Bangkok, and Mumbai being submerged.
A study published in the journal Nature Geoscience notes that the number of cracks in the glacier has sharply increased in recent years. Experts believe that vortices formed under the ice are drawing in warm water currents, accelerating the melting process.
Data shows that since the 1980s, the Thwaites Glacier has lost more than 600 billion tons of ice. As global warming continues, such processes may also be observed in other regions of Antarctica.
The Thwaites Glacier is 120 kilometers wide, with a total area of 190,000 square kilometers. This area is almost equivalent to the U.S. state of Florida.
The loss of the glacier could have catastrophic effects not only on large cities but also on low-lying countries such as the Maldives, Tuvalu, Kiribati, and Polynesia. Scientists had already warned in early 2025 about the possibility of the ice shelf beneath the glacier collapsing within the next decade.
This process poses a serious threat to the global ecological balance.